1. The First Locks in Ancient Egypt
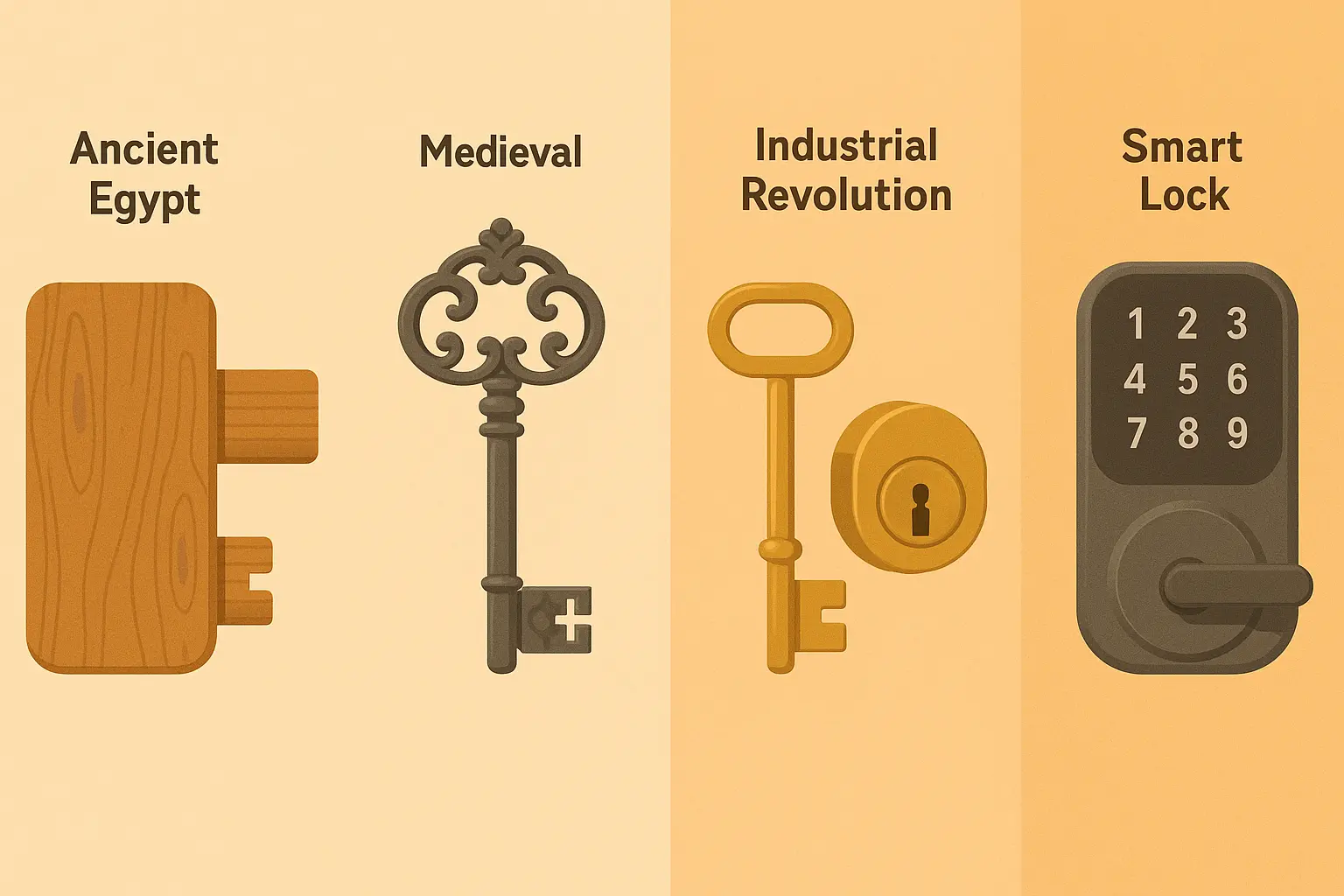
The earliest known locks appeared over 4,000 years ago in ancient Egypt. These were large wooden mechanisms, using simple pins that could be lifted with a specially shaped wooden key. While basic, they introduced the revolutionary idea of controlling access - something humans had never formalized before. You can read more in the History of locks in Ancient Egypt entry on Wikipedia.
These ancient Egyptian wooden locks were commonly installed on storage rooms and temple doors to protect grain, jewelry, and sacred treasures. By today's standards they were bulky and easy to bypass, yet in the history of locksmithing they marked a revolutionary step forward. For the first time, people used a mechanical device to control access and bring security into daily life.
Common Questions About Locksmith History
- When were the first locks invented? The earliest locks appeared in Ancient Egypt around 4,000 years ago, using wooden pins and large keys.
- How did locksmithing change over time? From medieval iron craftsmanship to the Industrial Revolution's mass production, locks became the gold standard for home security.
- Are modern smart locks more secure? Today’s locksmiths integrate biometrics and encryption, blending traditional mechanics with 21st-century cybersecurity.
"Historians believe the very first locks in ancient Egypt were so large that keys had to be carried on the shoulder like tools. It shows how important security was, even thousands of years ago."

2. Medieval Iron Keys and Master Craftsmanship
During the Middle Ages, locksmithing became less about simple function and more about craftsmanship and status. Keys were no longer just tools - they were symbols of power. Large iron keys were carried by castle guards, church officials, and wealthy merchants, often decorated with intricate designs that reflected the prestige of their owners. Unlike the bulky wooden mechanisms of ancient Egypt, medieval locks and keys were made of iron and steel, built to withstand force and tampering. These creations represented both practical security and artistic expression, turning locksmiths into respected artisans across Europe.
- Iron and steel keys replaced wood, offering strength and durability.
- Ornamental designs - keys often had engravings, patterns, or family crests.
- Used in castles, cathedrals, and merchant houses for valuables and authority.
- Showed the rise of locksmiths as skilled craftsmen with social status.
3. The Industrial Revolution and Mass-Produced Locks
The Industrial Revolution in the 18th and 19th centuries changed locksmithing forever. For the first time, locks could be mass-produced using new machines, making them more affordable and widely available to ordinary families, not just royalty or merchants. Factories in England, France, and the United States began producing thousands of locks every year, leading to an explosion in home and business security.
This era also saw a wave of innovations and patents. Inventors like Robert Barron, who created the double-acting tumbler lock in 1778, and Jeremiah Chubb, who patented the Chubb detector lock in 1818, set the stage for modern security. These locks were harder to pick and became the standard in banks, government offices, and private homes. The combination of mass production and improved design meant locksmithing was no longer just an art - it became an essential industry powering everyday life.
- Mass production made locks affordable for the average household.
- Key patents like Barron's double tumbler and Chubb's detector lock improved security.
- Factories in England, France, and the U.S. drove innovation worldwide.
- Locksmithing shifted from artisan craft to industrial profession.

"When Jeremiah Chubb introduced his detector lock in 1818, it was hailed as unpickable. The government even offered rewards to anyone who could break it - and for years, no one could."
4. The Rise of Smart Locks, Biometrics, and Digital Security
In the 21st century, locksmithing entered the digital age. Smart locks connected to smartphones, biometric systems using fingerprints or facial recognition, and Bluetooth-enabled deadbolts are now common in homes and businesses worldwide. These devices offer convenience - remote access, digital codes for family members or contractors, and integration with smart home systems - but they also introduce new challenges like hacking, battery life, and software vulnerabilities. For an independent review of leading smart lock models, Consumer Reports provides detailed testing and comparisons.
The modern locksmith is no longer just a metalworker but a security consultant, helping families, property managers, and companies choose between traditional deadbolts and advanced electronic systems. The future of locksmithing blends centuries-old mechanical expertise with cutting-edge technology, proving that the profession continues to evolve.
- Smart locks controlled by apps and cloud services are replacing traditional keys.
- Biometric access - fingerprints, facial recognition, and even retina scans - is entering mainstream security.
- IoT integration allows locks to connect with alarms, cameras, and voice assistants.
- Locksmiths today combine mechanical skills with cybersecurity awareness.
5. The Future of Locksmithing - AI, Quantum Locks, and Beyond
What does the future of locksmithing look like? Imagine doors that unlock only when an AI algorithm recognizes your heartbeat, or quantum-encrypted locks that are mathematically impossible to pick. Researchers are already exploring neural interface keys - systems that read brainwave patterns - while startups experiment with blockchain-based access control for apartments and offices.
Locksmiths of tomorrow may spend less time cutting metal and more time configuring cyber-physical security systems. Just as ancient Egyptians pioneered wooden locks and the Industrial Revolution gave us mass-produced deadbolts, the coming decades could redefine what "a key" even means. Whether through biometrics, AI-driven monitoring, or quantum security protocols, the core mission remains the same: keeping families, businesses, and communities safe in an ever-changing world.
- AI-powered locks that learn user behavior and detect threats in real time.
- Quantum encryption making lockpicking virtually impossible.
- Blockchain access systems for secure, transparent digital keys.
- Next-generation locksmiths as cybersecurity experts as much as technicians.
"In the near future, locks may not need keys or codes at all. Imagine doors that open only when your unique heartbeat or brainwave pattern is recognized. The line between locksmithing and cybersecurity is already starting to blur."
Professional help when you need it
From the first wooden locks in ancient Egypt to today's AI-powered smart locks, one thing hasn't changed - people still need trusted locksmiths when something goes wrong. If you're facing a stubborn lock, lost keys, or want advice on modern home and business security, a certified local locksmith near you can help. Get expert inspection, professional repairs, and peace of mind knowing your locks are reliable in every era.
Final Thoughts
"From the wooden locks of ancient Egypt to today's smart and biometric systems, the story of locksmithing proves one thing - security is always evolving. Whatever the future brings, trusted locksmiths will remain the link between technology and peace of mind."